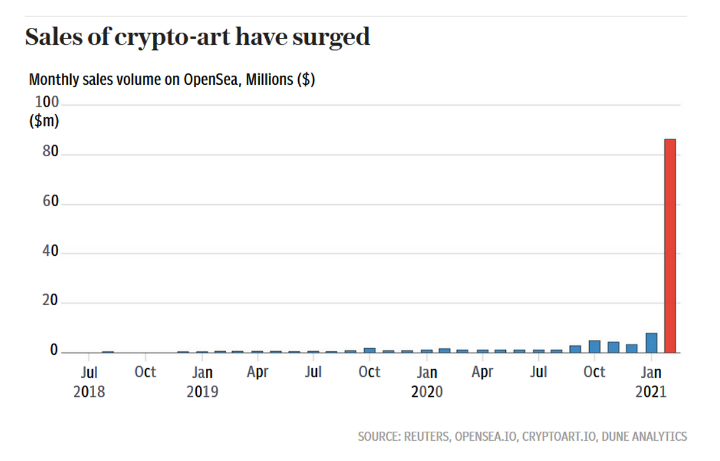
The Rise of NFTs and How Enterprise Blockchain Could Be Capitalizing
In times past, creatives and other professionals had problems monetizing their work. They had to be part of a larger company or agency that was capable of promoting them to get their works of art in the hands of buyers. This was a problem as these companies shared the money made and the rights to the works these professionals produced. Creatives were always short-changed until the inception of the non-fungible token (NFT).
This new type of digital asset helps creatives and other professionals have complete rights and monetization over their works. But, to better understand how NFTs help professionals, it is important to understand what they are first.
What Are NFTs?
An NFT is a unique digital representation of a “real object” on a blockchain. NFTs cannot be traded for another token—hence the term “non-fungible”.
The real object that is tokenized in this manner can range from something as real as a painting to as digital as a video clip. The essence of the non-fungible token technology is to provide the creator with proof of ownership in an immutable way—on the blockchain.
Without this layer of protection, pirated copies of these objects can be produced and distributed without the knowledge of the owner. So, to protect the owner’s right and differentiate which is the original document from the copies, NFTs are defined by their unique identifying codes.
To better understand the non-fungible token concept, imagine it as an autograph from a celebrity on a piece of paper. Consider the owner a celebrity in this case. Just like with autographs, the owner can create as many copies of the NFTs as they want. But, unlike autographs where someone can forge a signature, owners can create copies of non-fungible tokens without the consent of the seller.
Types of Non-Fungible Tokens
The category an NFT falls into depends on its usage. Most NFTs are built on the same Ethereum-based blockchain platform. However, the platform is scalable enough to serve a wide range of purposes. Therefore, there are different types of this class of digital assets.
Arts
NFT arts provides a good platform for artists to sell their artworks. Artists need to mint their artworks on the blockchain platform after creating them. Minting or tokenizing artworks helps to identify the real owner. The blockchain platform also shows the history of owners of NFTs.
It is up to the artist to sell the original artwork or copies of it. NFT arts do not take away royalty benefits from artists, who can also make royalties every time the artwork is sold. This can be done if the artist still retains the creator’s share of the artwork.
Collectibles
Collectibles are another item that has incorporated the use of NFTs. Before the NFT inception, collectibles were often sold at auctions to generate money for the owners and sometimes even governments.
Just like in the case of artworks, collectibles lacked an easy means of differentiating originals from fakes and copies. With the introduction of NFTs, buyers have now assured ownership through blockchain secure authentication.
Entertainment
The entertainment industry is the home of piracy. People share digital files across platforms. Some even make changes to the file. There is a particular video of a little girl dancing. This video has been edited to have four different background music. The editing is so good that it is hard to tell which is the original one.
NFT entertainment provides a more profitable way for entertainers to monetize their work. NFT entertainment includes tokenized forms of digital copies of music or videos. Unlike the case of the video mentioned above, NFT videos cannot be edited without the permission of the primary creator.
Sports
Before the incorporation of the non-fungible token technology, football clubs have tokenized fan support to enable the team to raise funds. This was a necessary decision to keep clubs afloat after the devastating effects of the pandemic.
But, unlike club tokens, sports NFTs cannot be traded for each other. Sport NFTs are digital representations of actual events—like the replay of a particular goal or the ball used in playing an important match—and have been gaining popularity since their emergence.
Real Estate
The real estate industry is also employing the use of NFTs and blockchain in authentication to secure the ownership of stakeholders. Instead of paper documents that can be forged, NFT is created and signed using software. With its unique identifying code, it will be far easier to identify which document is real and which is fake.
Benefits of Non-fungible Tokens
Non-fungible tokens offer a lot of potential to a wide variety of industries, as they are a major means of ensuring the safety of the ownership of an item. Here are some benefits of NFTs.
NFTs Are Easy to Verify
As stated earlier, NFTs help to resolve disputes of ownership and originality. Before the inception of the non-fungible token standard, it took an expert to differentiate between an original artwork and a fake. It was also very difficult to tell which artwork was the original and which was the copy.
Items like video clips, printed documents, and the likes are almost impossible to differentiate. With the introduction of NFTs, it is far easier to differentiate the original item from its copy. This can be done by assessing its unique identifying code. NFTs also show the history of their ownership.
They Are Harder to Destroy
NFTs are almost impossible to tamper with. The nature of non-fungible token technology protects these digital assets by ensuring that the owner is always in charge, not the third-party platform. If you buy gaming NFT, for example, it is stored with you and not on the gaming platform.
NFTs run on smart contracts that are used to store their data on a blockchain platform. Their self-executing nature diminishes the chances of human error and enhances ownership safety.
Disadvantages of Non-fungible Tokens
Despite their enormous potential, NFTs still have certain drawbacks that lead to skepticism around purchasing NFTs. Below are some of them.
NFTs Are Not Divisible
Unlike fungible cryptocurrencies, NFTs are bought as a whole and cannot be divided into smaller units. While this may be an advantage for some (potential) owners, it can still be a disadvantage for others. The implication of not being able to divide NFTs into smaller units means that the entry point of a non-fungible token exchange is very high. You are either able to buy it or you are not.
No Pricing System for NFTs
The price and value of NFTs are determined by the person who is buying them. Unlike fungible cryptocurrencies where trades and purchases regulate the market, there are no real price regulations in NFTs. The items the NFTs represent are only as good as the amount of money the buyer is willing to pay for it.
While this may not matter to a die-hard collector, it can pose a big problem to an investor. If an investor cannot determine the proposed profit for an item, they may not want to invest in it at all.
The future of non-fungible tokens will be the use of blockchain secure authentication like AIKON is proposing through its solutions like ORE ID—a universal authentication and authorization platform for blockchain—and ORE Vault—a shared enterprise wallet. This is essential considering that most hacks on blockchain platforms use the same process of getting passwords from owners of digital assets.
With the introduction of other blockchain-based means of authentication, NFTs will be much safer. It will also help blockchain to scale in growth and adoption. NFTs will foster enterprise blockchain adoption among major companies interested in entering the space.
Courtesy by:
Abhishek Bakshi
