Job Analysis
It is the process to hire a person and determine the duties and skill requirements for a particular job position.
Job Description
It is one product of job analysis, a list of a job’s duties, responsibilities, reporting relationships, working conditions, and supervisory responsibilities.
Job Specifications
It is another product of job analysis, a list of a job’s “human requirements,” that is, the requisite education, skills, personality, and so on.
Some types of information need to collect to conduct a job analysis, these include:
- Work activities (e.g. cleaning etc.)
- Human behaviors (e.g. deciding, writing, etc.)
- Machines, tools, equipment, and work aids
- Performance standards (To evaluate later)
- Job context (physical conditions, schedules)
- Human requirements
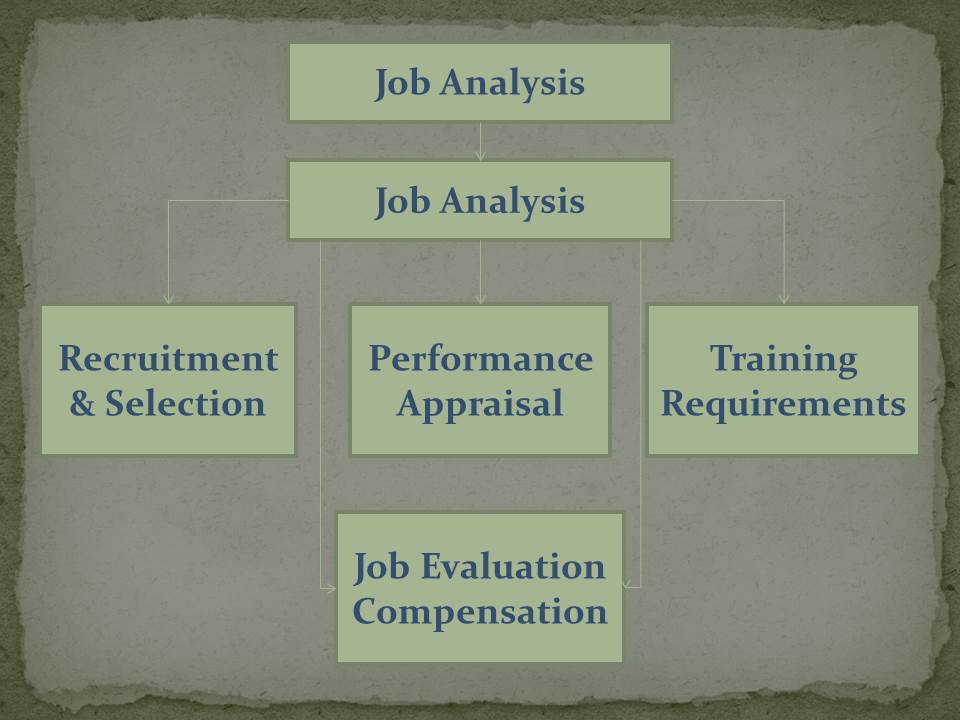
Usage of Job Analysis Information
The information collected during job analysis can be used for multiple purposes such as:
- Recruitment and Selection
- Compensation
- Performance Appraisal
- Training
- Discovering Unassigned Duties
The information can be used in below-mentioned steps:
- Decide how you’ll use the information.
- Review relevant background information.
- Select representative positions.
- Actually analyze the job.
- Verify the job analysis information.
- Develop a job description and job
Organization chart
Organization Chart is a flowchart that displays the organization-wide distribution of work, with titles of each position and interconnecting lines that show reporting and communication framework.
Process chart
Process Chart is a work flow chart that shows the flow of inputs to and outputs from a particular job.
Methods of Collecting Job Analysis Information:
1. Interview
- Information sources
- Individual employees
- Groups of employees
- Supervisors with knowledge of the job
- Advantages
- The quick, direct way to find overlooked information.
- Disadvantages
- Distorted information
- Interview formats
- Structured (Checklist)
- Unstructured
- Guidelines for Interview
- Supervisor and the job analyst should work together to recognize the workers who know the job best.
- Establish a quick connection with the interviewee.
- Follow a structured guide or checklist, one that lists open-ended questions and provides space for answers.
- Ask the worker to list his or her duties in order of importance and frequency of occurrence.
- Review and verify the data after completing the interview.
2. Questionnaires
- Information source
- Questionnaires shall be filled out by employees to describe their job-related duties and responsibilities.
- Questionnaire formats
- Structured checklists
- Opened-ended questions
- Advantages
- Fast and proficient way to gather information from large numbers of employees
- Disadvantages
- Expense and time used up in preparing and testing the questionnaire
3. Observation
- Information source
- Observing and noting the physical activities of employees during them go about their jobs.
- Advantages
- Provides first-hand information
- Reduces distortion of information
- Disadvantages
- Time-consuming
- Difficulty in capturing the entire job cycle
- Of little use, if a job involves a high level of mental activity
4. Participant Diary/Logs
- Information source
- Workers keep a sequential diary/ log of what they do and the time spent in each activity.
- Advantages
- Generates a more comprehensive picture of the job
- Employee involvement
- Disadvantages
- Misrepresentation of information
- Depends upon employees to perfectly recall their activities
Job Analysis Quantitative Techniques
- Position Analysis Questionnaire (PAQ)
- A questionnaire used to collect quantifiable data concerning the duties and responsibilities of various jobs.
- The PAQ comprises six divisions, with each division containing numerous job elements. The divisions include:
Information input – Where and how does the worker get information to do the job?
Mental process – What levels of reasoning are necessary for the job?
Work output – What physical activities are performed?
Relationships with others – What kind of relationships are required to perform the job?
Job context – What working conditions and social contexts are involved?
Other – What else is relevant to the job?
- Department Of Labor (DOL)
- A standardized procedure by which different jobs can be quantitatively rated, classified, and compared.
- Functional job analysis
- FJA takes into account the magnitude to which instructions, reasoning, judgment, mathematical and verbal ability are compulsory for performing job tasks.
Also, visit Human Resource Management – Part 1
Also, visit Human Resource Management – Part 2